Victorian casual workers to receive personal leave pay

In what may be just a political stunt given it’s an election year, the Victorian Government has announced that from March 2022, some casual workers will be able to claim personal leave pay. This is very unusual because casual workers are not entitled to sick leave, rather they receive a 25% loading on top of their hourly rate in lieu of holiday and sick pay. The Government is doing this to help stop the spread of COVID-19 and other diseases as it is known that casual staff will attend work when they are ill to avoid loss of wages and shifts. As per their website, their main reason for introducing this new payment is to allow casual workers to take time off if they are ill or if they need to care of family members because in their words, “no worker should have to choose between a day’s pay and their health, or the health of a loved one”. This blog will look at the details behind this scheme and ask the question, “Is this payment fair?”
What is the Victorian Sick Pay Guarantee?
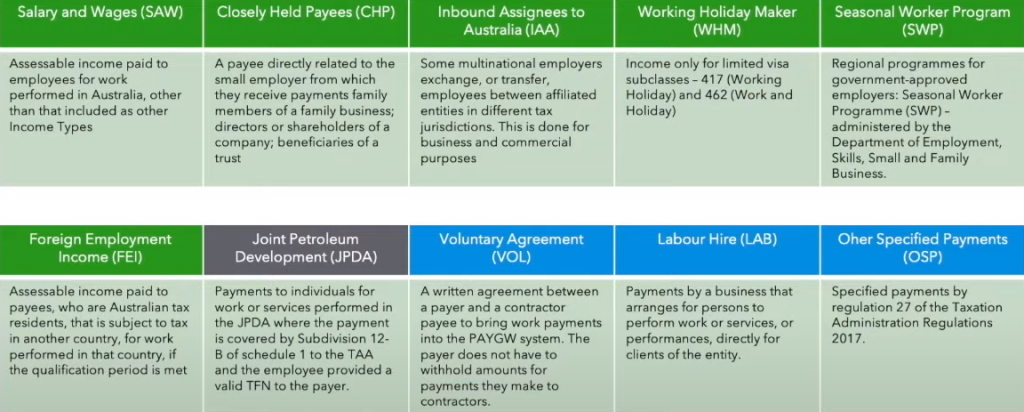
The Victorian Sick Pay Guarantee (VSPG) is a government-paid initiative that allows for some casual and contract workers as listed below, to receive 38 hours of personal leave pay at the national minimum wage (currently $20.33/hour). The program will run as a trial for 2 years after which time, it may become an industry levy on employers. The scheme is active now and those wanting to apply for the leave payment can do so here.
| JOB | TYPE OF WORK |
|---|---|
| Hospitality workers | Providing services to patrons of hotels, bars, cafes, restaurants, and similar venues. |
| Food preparation assistants | Preparing food in fast food establishments, assisting food trades workers and service staff to prepare and serve food, cleaning food preparation and service areas. |
| Food trades workers | Baking bread and pastry goods; preparing meat for sale; planning, organising, preparing and cooking food for dining and catering establishments. |
| Sales support workers | Providing assistance to retailers, wholesalers and sales staff by operating cash registers, modelling, demonstrating, selecting, buying, promoting and displaying goods. |
| Sales assistants | Selling goods and services directly to the public on behalf of retail and wholesale establishments. |
| Other labourers who work in supermarket supply chains | Including workers who fill shelves and display areas in stores and supermarkets; load and unload trucks and containers, and handle goods and freight. |
| Aged and disability carers | Providing general household assistance, emotional support, care and companionship for aged and disabled persons in their own homes. |
| Cleaners and laundry workers | Cleaning vehicles, commercial, industrial and domestic premises, construction sites and industrial machines, and clothing and other items in laundries and dry-cleaning establishments. |
| Security officers and guards | Providing security and investigative services to organisations and individuals, excluding armoured car escorts and private investigators. |
Is this fair for employers?
It’s important to remember that for the first 2 years, this scheme will be paid by the Government, not employers. Should it continue, however, it is believed that employers will need to pay an industry levy that will cover the VSPG for casual staff. Therefore, employment costs will increase, placing further financial pressure on employers. Employers are already paying a 25% loading on top of basic wages for casual staff which is supposed to cover their sick and holiday pay. Some would say that the addition of the VSPG is double-dipping, given that a casual worker will receive both the loading and the sick payment. If this scheme continues, some employers may be pushed to employ part-time or full-time staff only in an attempt to avoid increased costs brought on by using casual employees.
Is this fair for employees?
Certainly, it can be argued that casual employees are an “at-risk” demographic. They are subject to reduced hours, unstable employment and increased difficulty in maintaining a robust credit record. They do not have the same job security as their part or full-time counterparts. As they generally do not work full-time hours, their income is greatly reduced and even though they are in receipt of the 25% loading, they do not have the ability to save this loading for sick days, as they need every cent just to live! Many are working paycheck to paycheck in order to pay rent and put food on the table. This being the case, it is understandable that some would choose to go to work sick, rather than lose wages, shifts and/or their job. With this in mind, the VSPG is fair for these employees. They can maintain their income and avoid spreading viruses like COVID-19. This is good for everyone.
Here’s what I think
I do like the idea of the VSPG. I am sure it will really help many casual workers (double-dipping or not). However, I think it’s just a temporary solution because once the VSPG payment is used up (the 38 hours), it is likely that workers will go back to attending work when they are ill. I’ve had a think about it and here are some alternative solutions I’ve come up with. Casual workers could:
- Opt-in for loading or leave accruals, but not both.
- Receive a smaller loading and accrue leave as well.
- Apply for a top-up payment from the Government, when wages fall below a certain point for a particular period.
These are just some ideas jumping around in my head, but as I write this, I am left wondering if the double-dipping issue is the real problem here. Perhaps the real issue is not what is paid to casual staff, but rather, how much.
I believe, underlying the need to top up casuals’ pay with the VSPG and/or loadings, is a wage level problem. If these employees were paid adequately in the first place, then perhaps there would be no need for either the loading or the VSPG.
For many casual employees, wages are just too low, loading or no loading. Many who are students, carers or parents cannot work full-time hours and, as such, are subject to very low incomes. In my opinion, we need to look at wage growth and inflation before offering bandaid solutions such as the VSPG. Wages need to be kept in line with inflation. Simple as that. The Government that makes this happen, will get my vote this election year. Sadly, I think I’ll be left wanting…
Victorian casual workers to receive personal leave pay Read More »